Electric vs. Gas Transfer Pumps: Making the Right Choice
Transfer pumps are essential tools used in a wide range of industries, from agriculture and construction to manufacturing and water management. These versatile devices are designed to move liquids, slurries, or other fluids from one location to another, facilitating various processes and operations. The selection of the right type of transfer pump is crucial, as it can significantly impact the efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and overall success of a project or application.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore the key differences between electric and gas-powered transfer pumps, examining their respective advantages, disadvantages, and the factors to consider when choosing the most suitable option for your needs. By understanding the unique characteristics and capabilities of these two pump types, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your specific requirements and ensures optimal performance.
Key Takeaways
- Electric transfer pumps are powered by electricity and are often more convenient and easier to use than gas-powered transfer pumps.
- Electric transfer pumps have the advantage of being quieter, more environmentally friendly, and easier to maintain than gas-powered transfer pumps.
- However, electric transfer pumps may not be as powerful as gas-powered transfer pumps and may not be suitable for use in remote locations without access to electricity.
- Gas-powered transfer pumps are powered by gasoline or diesel and are often more powerful and suitable for use in remote locations where electricity may not be available.
- When choosing between electric and gas-powered transfer pumps, it’s important to consider factors such as power requirements, portability, and the specific needs of the job or project.
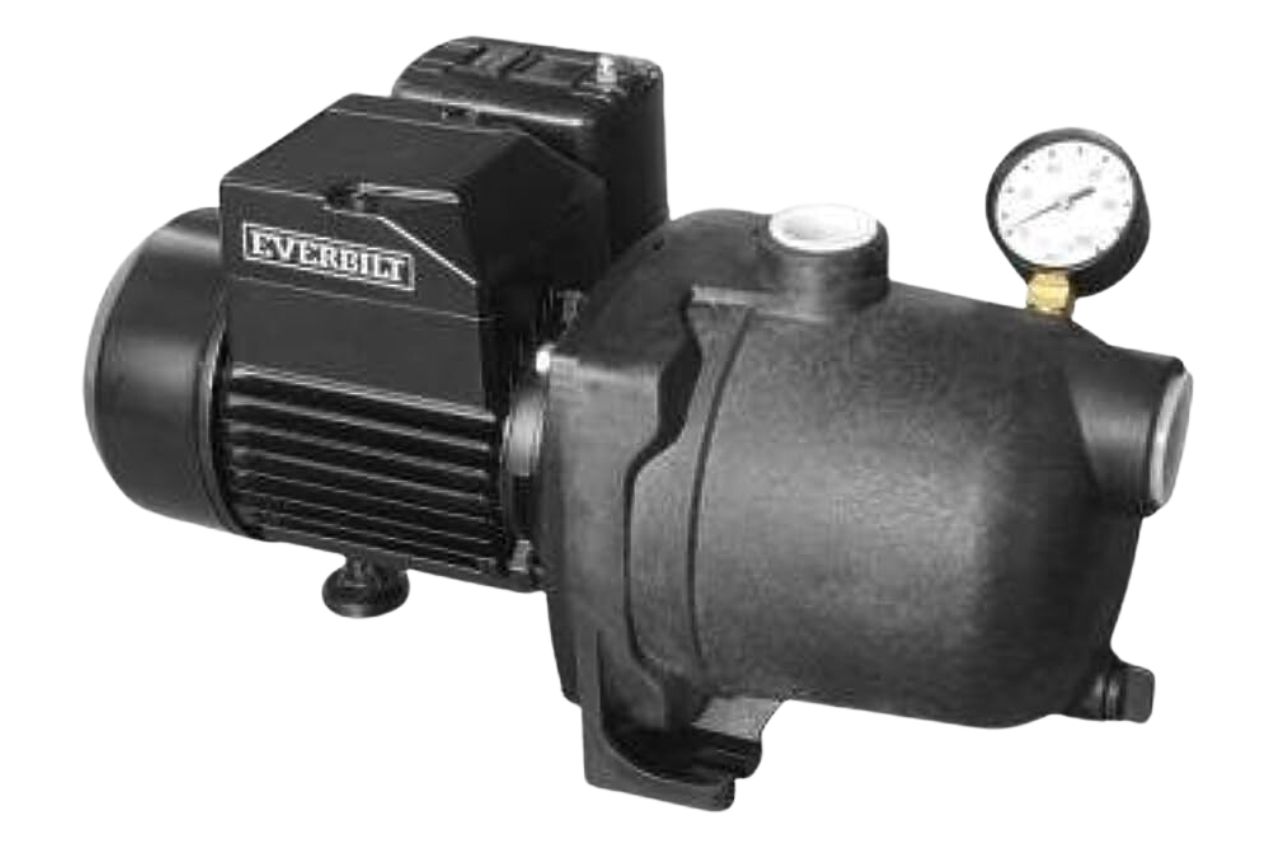
Understanding Electric Transfer Pumps
Electric transfer pumps are powered by an electric motor, which is typically connected to a power source such as a wall outlet or a portable generator. These pumps offer a range of benefits that make them a popular choice in various applications. The electric motor provides a reliable and consistent power source, ensuring smooth and efficient operation. Additionally, the absence of a combustion engine means that electric transfer pumps are generally quieter and produce fewer emissions, making them a more environmentally friendly option.
The performance and efficiency of electric transfer pumps are influenced by several factors, including the motor size, impeller design, and the quality of the electrical components. Larger motors, for example, can typically deliver higher flow rates and greater pressure capabilities, while the impeller design can impact the pump’s ability to handle different types of fluids and handle solids or debris. The quality of the electrical components, such as the wiring, switches, and control systems, can also play a crucial role in the overall reliability and longevity of the pump.
Advantages of Electric Transfer Pumps
One of the primary advantages of electric transfer pumps is their ease of use and maintenance. These pumps are generally simpler to operate, with fewer moving parts and less complex mechanisms compared to their gas-powered counterparts. This simplicity translates to reduced maintenance requirements, as there is no need to regularly service or replace components like spark plugs, air filters, or fuel systems. Additionally, the absence of a combustion engine means that electric transfer pumps are typically more environmentally friendly, producing no direct emissions and requiring less fuel or oil consumption.
Another significant advantage of electric transfer pumps is their quieter operation. The electric motor generates less noise than a gas-powered engine, making these pumps more suitable for use in noise-sensitive environments, such as residential areas or indoor settings. This quiet operation can be particularly beneficial in applications where noise levels need to be minimized, such as in construction sites, agricultural operations, or water treatment facilities.
In the long run, electric transfer pumps can also offer potential cost savings. While the initial purchase price may be higher than that of gas-powered pumps, the reduced fuel and maintenance costs associated with electric models can offset this difference over time. Additionally, the increased energy efficiency of electric pumps can lead to lower operating costs, further contributing to the overall cost-effectiveness of these devices.
Disadvantages of Electric Transfer Pumps
One of the primary drawbacks of electric transfer pumps is their dependence on a reliable power source. These pumps require a consistent supply of electricity to function, which can be a limitation in remote or off-grid locations where access to power may be limited or intermittent. In such scenarios, the lack of a self-contained power source can restrict the mobility and portability of the pump, potentially limiting its usefulness in certain applications.
Another potential disadvantage of electric transfer pumps is their potential limitations in terms of flow rate and pressure capabilities. While advancements in motor and impeller technology have improved the performance of these pumps, they may still fall short in applications that require exceptionally high flow rates or pressure demands. In such cases, gas-powered transfer pumps may be better suited to meet the specific requirements of the task at hand.
Additionally, the reliance on electrical power can make electric transfer pumps vulnerable to power outages or disruptions, which can temporarily halt operations and potentially cause issues in time-sensitive or critical applications. This dependency on a stable power supply is an important consideration when selecting the appropriate transfer pump for your needs.
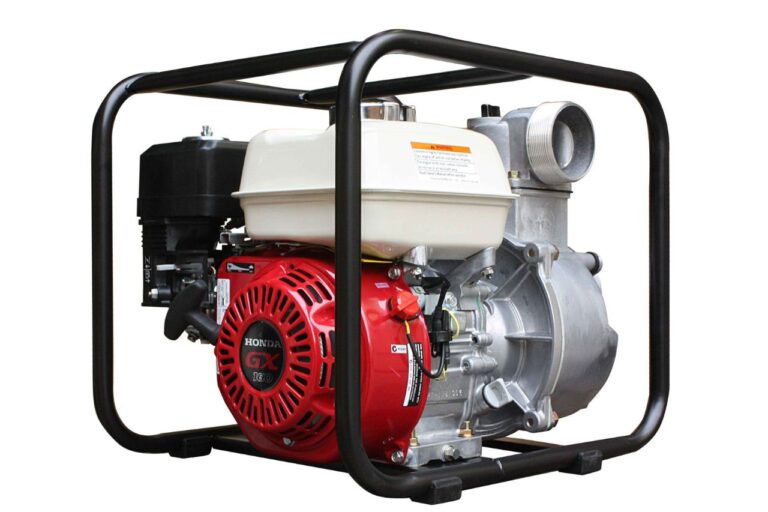
Understanding Gas-Powered Transfer Pumps
| Transfer Pump Type | Electric | Gas-Powered |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Electricity | Gasoline or Diesel |
| Portability | Less portable, requires power outlet | More portable, no power outlet needed |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, lower operating cost | Lower initial cost, higher operating cost |
| Environmental Impact | Lower emissions, quieter operation | Higher emissions, noisier operation |
Gas-powered transfer pumps are equipped with an internal combustion engine, typically fueled by gasoline or diesel, which provides the power to drive the pump’s impeller and move the fluid. These pumps are often favored for their increased mobility and portability, as they do not require a direct connection to an electrical power source. The self-contained nature of gas-powered transfer pumps makes them well-suited for use in remote or off-grid locations, where access to electricity may be limited or unavailable.
The performance and efficiency of gas-powered transfer pumps are influenced by factors such as the engine size, fuel efficiency, and the design of the pump’s components. Larger engines, for example, can typically deliver higher flow rates and greater pressure capabilities, while advancements in fuel efficiency can help to reduce operating costs and environmental impact. The quality and design of the pump’s impeller, housing, and other critical components can also play a significant role in the overall performance and reliability of the device.
Advantages of Gas-Powered Transfer Pumps
One of the primary advantages of gas-powered transfer pumps is their increased mobility and portability. These pumps are self-contained and can be easily transported to different locations, making them well-suited for use in remote or off-grid applications, such as construction sites, agricultural operations, or disaster relief efforts. The independence from electrical power sources also allows gas-powered transfer pumps to be used in areas where access to electricity may be limited or unreliable.
Another key advantage of gas-powered transfer pumps is their ability to deliver higher flow rates and pressure capabilities compared to many electric models. This makes them well-suited for applications that require the movement of large volumes of fluid or the ability to overcome significant head pressures. This increased performance can be particularly beneficial in industrial, agricultural, or construction-related tasks that demand high-capacity fluid transfer.
Additionally, the independence from electrical power sources means that gas-powered transfer pumps can continue to operate even in the event of a power outage or disruption. This can be a critical advantage in emergency situations or applications where uninterrupted fluid transfer is essential, such as in disaster response or water management scenarios.
Disadvantages of Gas-Powered Transfer Pumps
One of the primary drawbacks of gas-powered transfer pumps is the increased noise and emissions associated with their internal combustion engines. These pumps tend to be louder than their electric counterparts, which can be a concern in noise-sensitive environments or when working in close proximity to others. Additionally, the combustion of fuel produces exhaust emissions, which can have environmental and health implications, particularly in enclosed or poorly ventilated spaces.
Another potential disadvantage of gas-powered transfer pumps is the higher maintenance requirements compared to electric models. The internal combustion engine, fuel system, and other components require regular servicing, such as oil changes, air filter replacements, and spark plug maintenance. This increased maintenance can lead to higher operating costs and the need for more specialized technical expertise to ensure the pump’s proper functioning.
Fuel availability and cost can also be a concern with gas-powered transfer pumps. In remote or rural areas, access to the appropriate fuel (gasoline or diesel) may be limited, and fluctuations in fuel prices can impact the overall operating costs of the pump. This can be a significant consideration, especially in applications where the pump is used extensively or for extended periods.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Transfer Pump
When selecting a transfer pump, whether electric or gas-powered, it is essential to carefully consider the specific requirements of your application. The first and most crucial factor to evaluate is the application and usage requirements, such as the necessary flow rate, pressure, and volume of fluid to be transferred. This information will help you determine the appropriate size and capacity of the transfer pump, ensuring that it can meet the demands of your specific task.
Another important factor to consider is the availability and accessibility of the power source. If you have reliable access to electrical power, an electric transfer pump may be the more suitable option. Conversely, if you need to operate the pump in remote or off-grid locations, a gas-powered model may be the better choice.
Portability and mobility requirements are also essential considerations. If you need to frequently move the pump to different locations or work in areas with limited access, a gas-powered transfer pump with its self-contained power source may be the more practical solution.
Additionally, it is crucial to evaluate the long-term maintenance and operational costs associated with each type of transfer pump. While electric pumps may have a higher initial purchase price, their reduced maintenance requirements and potential for cost savings in fuel and oil consumption can make them more cost-effective in the long run. Conversely, gas-powered pumps may have lower upfront costs but higher ongoing maintenance and fuel expenses.
Finally, environmental and noise considerations should not be overlooked. If you are operating in noise-sensitive areas or need to minimize the environmental impact of your fluid transfer operations, an electric transfer pump may be the preferred choice due to its quieter operation and reduced emissions.
Selecting the Right Transfer Pump for Your Needs
In conclusion, the choice between electric and gas-powered transfer pumps ultimately depends on the specific requirements and constraints of your application. Electric transfer pumps offer the advantages of ease of use, environmental friendliness, and potential cost savings, while gas-powered models excel in terms of mobility, higher flow rates, and independence from electrical power sources.
When evaluating your options, it is essential to carefully assess factors such as the required flow rate, pressure, and volume, the availability and accessibility of power sources, portability and mobility needs, maintenance and operational costs, and environmental and noise considerations. By thoroughly understanding the unique characteristics and capabilities of each pump type, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your specific requirements and ensures the optimal performance and efficiency of your fluid transfer operations.
Ultimately, the right transfer pump for your needs is the one that strikes the perfect balance between functionality, cost-effectiveness, and environmental sustainability, enabling you to achieve your goals with confidence and efficiency. By carefully considering the factors outlined in this article, you can make an informed decision that will serve your needs now and well into the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are transfer pumps used for?
Transfer pumps are used to move liquids from one place to another, such as transferring water from a well to a storage tank, or pumping fuel from a drum into a vehicle.
What are the main differences between electric and gas-powered transfer pumps?
The main difference is the power source. Electric transfer pumps are powered by electricity, while gas-powered transfer pumps are powered by gasoline or diesel fuel.
What are the advantages of electric transfer pumps?
Electric transfer pumps are generally quieter, easier to maintain, and produce zero emissions. They are also suitable for indoor use and are often more cost-effective in the long run.
What are the advantages of gas-powered transfer pumps?
Gas-powered transfer pumps are typically more powerful and portable, making them suitable for outdoor use and remote locations where electricity may not be readily available.
What factors should be considered when choosing between electric and gas-powered transfer pumps?
Factors to consider include the intended use, power requirements, portability, operating costs, and environmental considerations. It’s important to assess the specific needs of the application to determine which type of pump is most suitable.