Find the Right Reverse Osmosis System: Traditional vs. Tankless
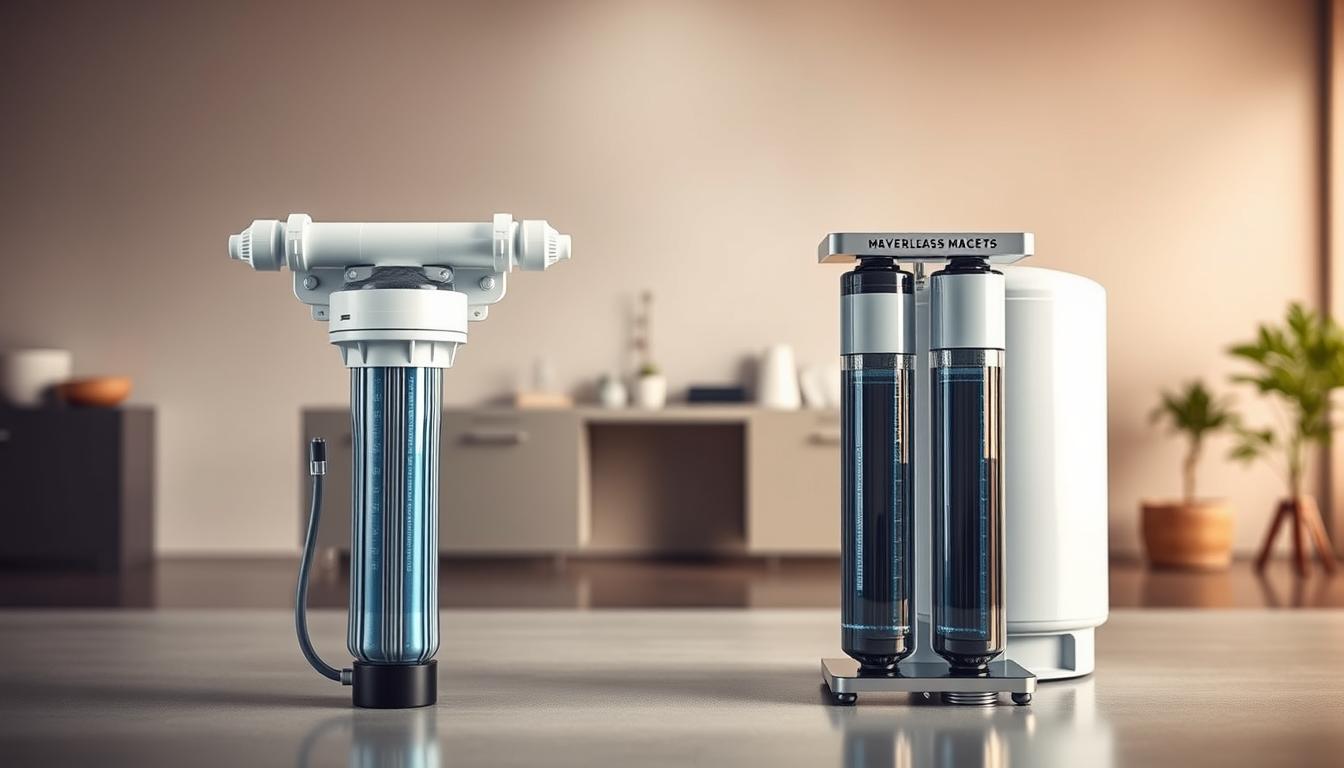
When it comes to Reverse Osmosis Water Filtration, choosing the right water filtration system can be daunting. With various options available, understanding the differences between traditional and tankless systems is crucial.
Both types have their advantages and disadvantages. Tankless systems offer continuous water flow, while traditional systems store filtered water in a tank. The choice between the two largely depends on your specific needs and preferences.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the differences between traditional and tankless RO systems.
- Learn about the benefits of continuous water flow in tankless systems.
- Discover how traditional systems store filtered water.
- Identify your specific needs for a water filtration system.
- Compare the advantages and disadvantages of both systems.
Understanding Reverse Osmosis Water Filtration
Understanding the mechanics of reverse osmosis is crucial for appreciating its effectiveness in water purification. Reverse osmosis (RO) is a water purification process that uses a semi-permeable membrane to remove ions, unwanted molecules, and larger particles from drinking water.
How Reverse Osmosis Works
The RO process involves several key stages. First, pre-filtration removes larger particles and sediments that could damage the semi-permeable membrane. Then, the water is forced through the semi-permeable membrane, which filters out impurities based on their size and charge, allowing clean water to pass through. Finally, post-filtration may be used to further polish the water, improving its taste and removing any remaining impurities.
Common Contaminants Removed
Reverse osmosis is effective against a wide range of contaminants. Some of the most common include:
- Lead: A toxic metal that can cause serious health issues, especially in children.
- Chlorine: Often used in municipal water treatment, chlorine can impart unpleasant tastes and odors.
- Dissolved Solids: RO can remove dissolved solids, improving the water’s taste and reducing its mineral content.
- Bacteria and Viruses: The semi-permeable membrane can block these pathogens, making RO water safer to drink.
Traditional Reverse Osmosis System and Tankless Reverse Osmosis System: Key Differences
Understanding the differences between traditional reverse osmosis systems and their tankless counterparts is crucial for making an informed decision.
The primary distinction lies in how each system stores and dispenses filtered water. Traditional systems rely on a storage tank to hold filtered water, whereas tankless systems provide on-demand filtration.
Storage Tank vs. On-Demand Filtration
Traditional RO systems use a storage tank that stores filtered water until it’s needed. This can lead to water sitting in the tank for periods, potentially affecting taste and quality. On the other hand, tankless RO systems filter water on demand, ensuring that water is fresh when dispensed.
The tankless approach eliminates the risk of stored water becoming stale or contaminated, a significant advantage for households prioritizing water quality.
Technology Evolution and Innovations
The evolution of RO technology has led to significant advancements in both traditional and tankless systems. Innovations such as improved membrane technology and more efficient pumping systems have enhanced overall system performance.
Recent advancements in RO technology advancements have focused on increasing water efficiency and reducing waste, making both types of systems more environmentally friendly.
As RO technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more efficient and effective systems in the future.
How Traditional Reverse Osmosis Systems Work
The operation of traditional reverse osmosis systems involves a complex interplay of various components working together to remove contaminants from water. These systems are designed to provide clean drinking water by leveraging a multi-stage filtration process.
Components and Design
Traditional reverse osmosis systems consist of several key components, including pre-filters, reverse osmosis membranes, and post-filters. The pre-filters remove larger particles and contaminants, protecting the RO membrane. The RO membrane is the heart of the system, filtering out dissolved solids and other impurities. Finally, post-filters polish the water, improving taste and removing any remaining odors.
Filtration Process and Storage
The filtration process in traditional RO systems is multi-staged. First, water passes through pre-filters to remove sediment and chlorine. Then, it is forced through the RO membrane, which removes up to 99% of dissolved contaminants. After filtration, the water is stored in a water storage tank until it’s needed. This tank holds the filtered water, allowing for on-demand access.
The use of a storage tank is a defining characteristic of traditional RO systems, allowing for a ready supply of filtered water. However, it also means that the water may sit in the tank for periods, potentially affecting taste and quality if not properly maintained.
How Tankless Reverse Osmosis Systems Work
Tankless Reverse Osmosis (RO) systems are revolutionizing water purification with their innovative on-demand filtration technology. Unlike traditional RO systems that store filtered water in tanks, tankless systems filter water in real-time, providing a continuous supply of clean drinking water.
Direct Flow Technology
Tankless RO systems utilize Direct Flow Technology, which allows water to flow directly through the filtration system without being stored. This technology not only saves space but also reduces the risk of water contamination that can occur in storage tanks. By filtering water on demand, tankless RO systems ensure that water is fresh and clean every time it’s dispensed.
Advanced Filtration Mechanisms
The effectiveness of tankless RO systems is largely due to their Advanced Filtration Mechanisms. These systems often employ high-efficiency RO membranes and additional filtration stages, such as activated carbon and UV light, to remove a wide range of contaminants. The result is water that is not only clean but also tastes good, with minimal loss of beneficial minerals.
In summary, tankless RO systems offer a modern, efficient, and effective solution for clean drinking water, leveraging direct flow technology and advanced filtration mechanisms to provide superior water quality.
Comparing Water Production and Efficiency
Understanding the efficiency and water production rates of RO systems is vital for households relying on these systems for clean drinking water. Both traditional and tankless RO systems have their strengths and weaknesses in terms of efficiency.
Flow Rates and Daily Capacity
The flow rate of an RO system determines how quickly it can produce filtered water. Traditional systems typically have a slower flow rate due to the need to fill a storage tank. In contrast, tankless systems provide water on demand, potentially offering faster flow rates. However, their daily capacity can be limited by their design and the household’s peak demand periods.
| System Type | Flow Rate (GPM) | Daily Capacity (Gallons) |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional RO | 0.5-1.0 | Up to 100 |
| Tankless RO | 1.0-2.0 | Variable, based on demand |
Water Waste Ratio Analysis
The water waste ratio is a critical factor in evaluating the efficiency of RO systems. Traditional RO systems tend to waste more water due to their storage tank design, which requires periodic flushing. Tankless systems, while potentially more efficient, still produce wastewater during the filtration process. However, some tankless models are designed to minimize this waste.
Efficient RO systems not only save water but also reduce the overall cost of ownership. When choosing between traditional and tankless RO systems, households must consider their specific needs and weigh the pros and cons of each system’s efficiency characteristics.
Water Quality Results Comparison
Understanding the nuances in water quality between traditional and tankless RO systems is essential for making an informed decision.
Both traditional and tankless RO systems are designed to remove contaminants and improve water taste and quality. However, their approaches differ, leading to variations in water quality results.
Contaminant Removal Effectiveness
The effectiveness of an RO system in removing contaminants is a crucial aspect of its overall performance. Tankless RO systems often have an edge in this regard due to their direct flow technology, which can reduce the chance of bacterial growth and contamination during storage.
In contrast, traditional RO systems store filtered water in tanks, which can potentially lead to re-contamination if not properly maintained.

Taste and Mineral Content
The taste and mineral content of water filtered through RO systems can vary. Traditional systems might remove more minerals due to the additional storage time, potentially affecting the taste.
Tankless systems, on the other hand, filter water on demand, preserving more of the water’s natural taste and potentially retaining more minerals.
Installation Considerations for Both Systems
Both traditional and tankless reverse osmosis systems have unique installation requirements that must be understood to ensure optimal functionality. The installation process can significantly impact the system’s performance, efficiency, and longevity.
Space Requirements and Placement Options
One of the critical factors in installing an RO system is assessing the available space. Traditional RO systems require more space due to the storage tank, which can be a limiting factor in smaller kitchens or areas with limited under-sink space. In contrast, tankless RO systems are more compact and offer greater flexibility in terms of placement, making them ideal for smaller spaces or whole-house installations.
When considering placement options, it’s essential to evaluate the proximity to a water supply line, drainage, and electrical outlets. Under-sink installations are common for both types, but whole-house configurations may require additional planning and potentially more complex plumbing.
DIY vs. Professional Installation
The decision to install an RO system yourself or hire a professional depends on several factors, including your plumbing knowledge, the complexity of the system, and local regulations. DIY installation can be cost-effective and rewarding for those with experience, but it may void the manufacturer’s warranty if not done correctly.
On the other hand, professional installation ensures that the system is set up correctly, minimizing the risk of leaks, improper connections, and other issues that could lead to water damage or reduced system performance. As noted by a water treatment expert, “Professional installation is not just about ensuring the system works; it’s about doing it safely and efficiently.”
“Hiring a professional to install your RO system can provide peace of mind and ensure that your system operates at its best.”
Ultimately, the choice between DIY and professional installation should be based on your comfort level with the installation process and the specific requirements of your chosen RO system.
Maintenance Requirements and Costs
Understanding the maintenance needs of your RO system can help prevent costly repairs and ensure clean drinking water. Proper maintenance involves regular filter replacements and system sanitization.
Filter Replacement Schedules and Procedures
Filter replacement is a critical maintenance task for RO systems. The frequency of replacement depends on the type of filter and the system’s usage. Typically, pre-filters and post-filters need to be replaced every 6 to 12 months, while the RO membrane may last 2 to 3 years.
Replacing filters is relatively straightforward. For traditional RO systems, this involves turning off the system, releasing pressure, and then replacing the old filters with new ones. Tankless RO systems follow a similar process, with some models featuring quick-change filter cartridges.
| Filter Type | Replacement Frequency | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-filter | Every 6 months | $20-$50 |
| RO Membrane | Every 2-3 years | $50-$100 |
| Post-filter | Every 12 months | $20-$50 |
System Sanitization and Long-term Care
System sanitization is crucial for preventing bacterial growth and maintaining water quality. This process typically involves flushing the system with a sanitizing solution. For both traditional and tankless RO systems, sanitization should be performed every 12 to 24 months.
Long-term care also includes checking the system regularly for signs of wear and tear, such as leaks or decreased water production. Ensuring that all connections are secure and that the system is properly installed can prevent many common issues.

Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-term Expenses
Evaluating the upfront and long-term expenses of RO systems is essential for making an informed decision. When considering a reverse osmosis system, it’s crucial to look beyond the initial purchase price and understand the total cost of ownership, including installation costs, operational expenses, and maintenance requirements.
Initial Purchase and Installation Costs
The initial investment in a reverse osmosis system includes the purchase price of the unit itself and the cost of installation. Traditional RO systems may have a lower upfront cost, but the need for a storage tank can add to the overall expense. In contrast, tankless RO systems often come with a higher initial purchase price, but they eliminate the need for a storage tank, potentially saving space and reducing overall installation costs.
As noted by industry experts, “The initial cost is just the beginning; understanding the long-term operational and maintenance costs is crucial for a comprehensive cost analysis.” Installation costs can vary depending on the complexity of the plumbing and electrical work required.
Operational Costs and Replacement Parts
Operational costs include energy consumption and the cost of replacement filters and parts over time. Tankless RO systems often have a more efficient filtration process, which can lead to lower operational costs in the long run. However, the cost of replacement parts, such as filters, can vary between traditional and tankless systems.
A detailed comparison of operational expenses reveals that while traditional systems may have lower initial costs, their long-term expenses can be higher due to the need for more frequent filter replacements and the energy required to maintain the storage tank.
Ideal Use Cases for Each System Type
Understanding the ideal applications for traditional and tankless RO systems is crucial for making an informed decision that meets your specific water filtration needs.
Best Scenarios for Traditional Systems
Traditional RO systems are particularly well-suited for larger households or applications where a high volume of filtered water is required. They are ideal for homes with multiple bathrooms or for families with high water consumption patterns. The storage tank in traditional systems allows for a ready supply of filtered water, making them suitable for households that need immediate access to filtered water without waiting for the filtration process to complete.
Additionally, traditional RO systems can be beneficial in situations where the incoming water pressure is low. The storage tank can be filled during periods of lower demand, ensuring a steady supply of filtered water even when the incoming pressure is not ideal.
When Tankless Systems Make More Sense
Tankless RO systems, on the other hand, are more suitable for smaller households or installations where space is limited. Without the need for a storage tank, tankless systems can be more compact and flexible in terms of installation options. They are also generally more modern and can offer a continuous supply of filtered water, albeit at a slower rate than traditional systems with storage tanks.
Tankless systems are also advantageous in scenarios where water quality is a significant concern, and on-demand filtration is preferred. They reduce the risk of water stagnation in the tank, potentially offering fresher filtered water.
Conclusion
After comparing traditional and tankless reverse osmosis systems, it’s clear that each has its strengths and weaknesses. The key to Choosing the Right RO System lies in understanding your specific needs and preferences.
A RO System Comparison Summary reveals that traditional systems are often more affordable upfront but may waste more water and require more maintenance. Tankless systems, on the other hand, offer on-demand filtration, reduced waste, and a more compact design.
When deciding between these two options, consider factors such as your household’s water usage, available installation space, and budget for maintenance and replacement parts. By weighing these factors, you can make an informed decision that suits your lifestyle and ensures access to clean drinking water.
Ultimately, the best RO system for you will depend on your unique circumstances. By considering the key differences and trade-offs between traditional and tankless systems, you can choose the solution that best meets your needs.