The Basics: How Does a Backflow Preventer Work?
Backflow preventers are vital for maintaining clean and safe water. They prevent the reverse flow of water, keeping contaminants out of the main water supply. In this article, we’ll explore how backflow preventers work and their importance in safeguarding water quality. Discover why these devices are crucial for maintaining clean and healthy water in your home or business.
Key Takeaways:
- A backflow preventer is a device that ensures water flows in only one direction by utilizing valves and check mechanisms.
- The most common type of backflow preventer is the reduced pressure zone (RPZ) device, which has two check valves and a relief valve.
- Different types of backflow preventers include RPZ backflow preventers, double check valve assemblies (DCVAs), pressure vacuum breakers (PVBs), atmospheric vacuum breakers (AVBs), and spill-resistant vacuum breakers (SVBs).
- Indicators of a faulty backflow preventer include decreased water pressure, contaminated water, leaks or dripping, and excessive pressure.
What is a backflow preventer?
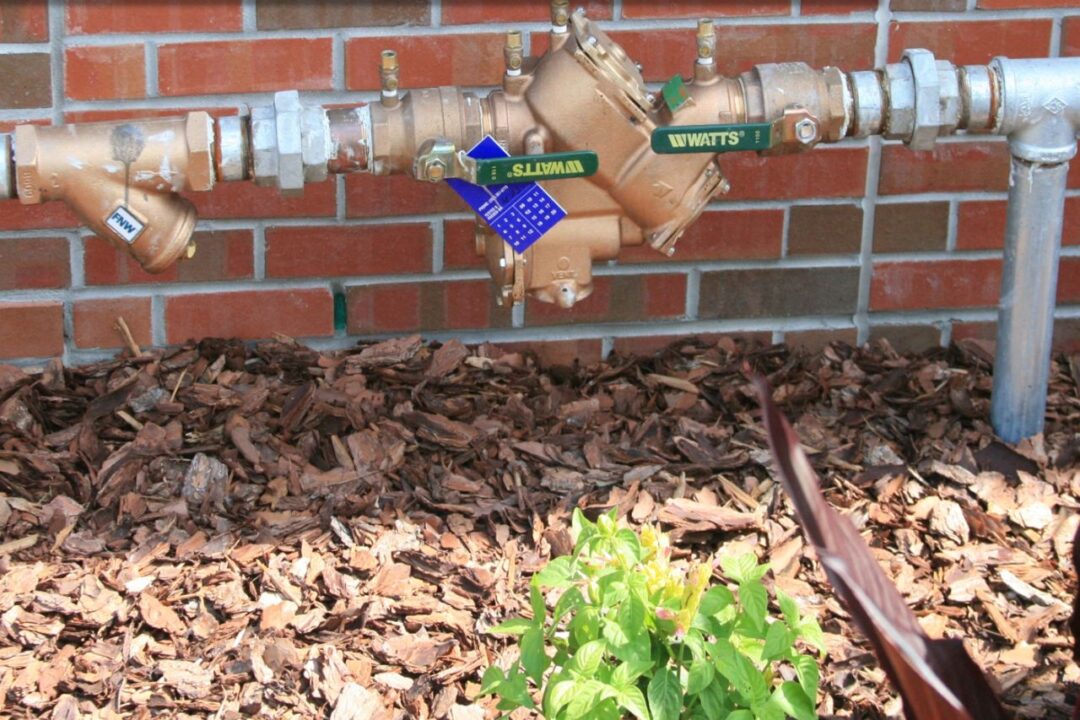

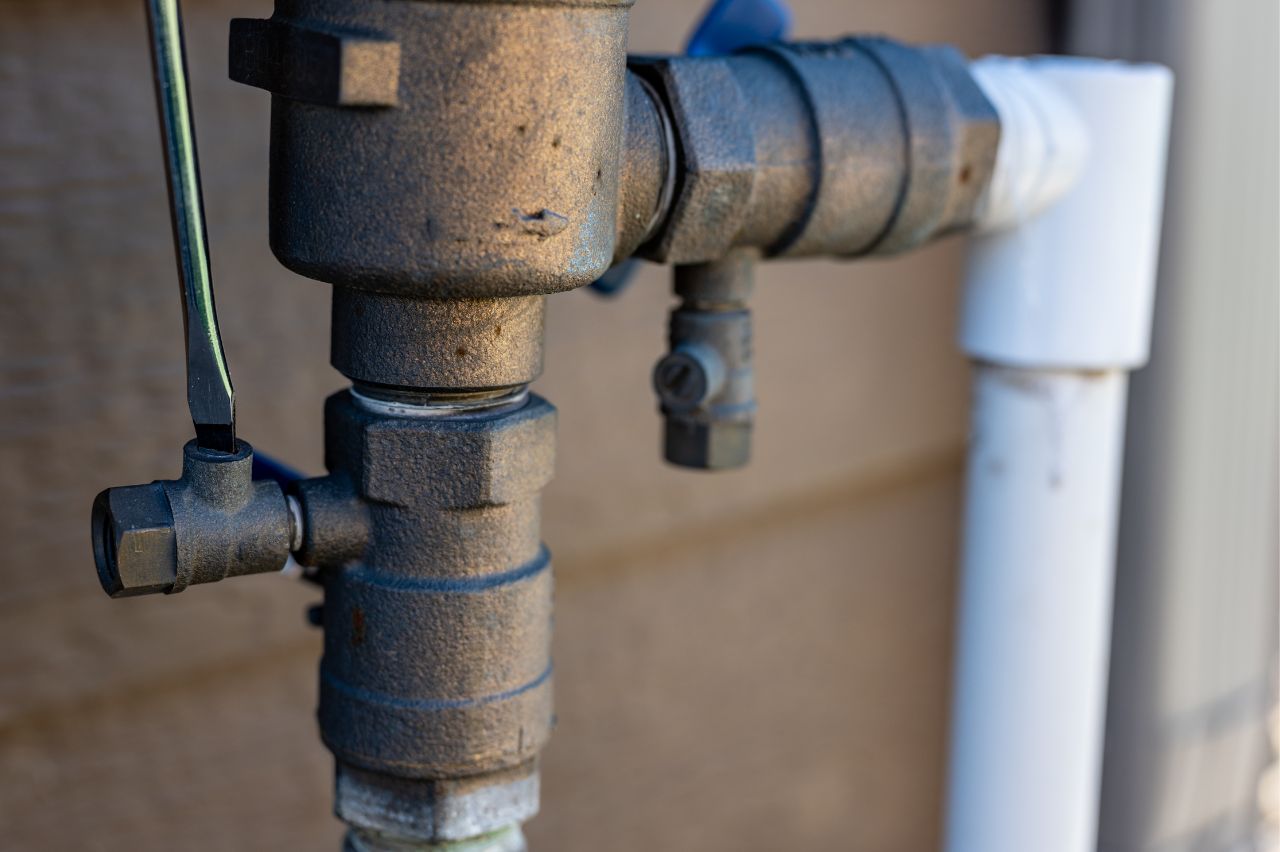
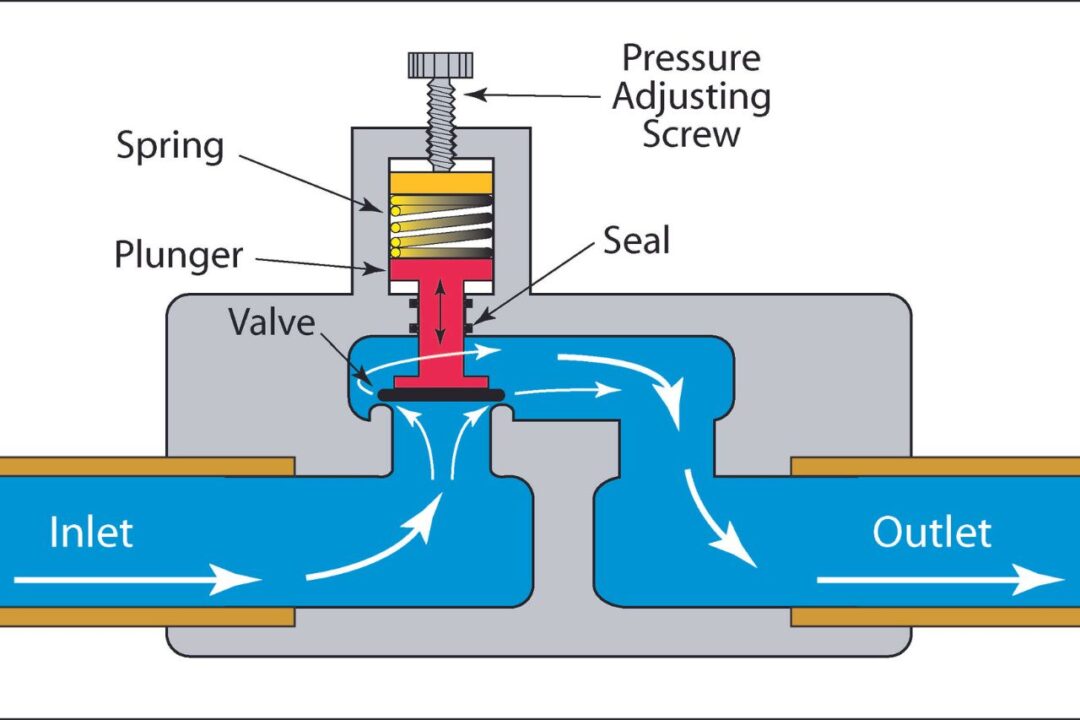
A backflow preventer is a mechanical device designed to prevent the reverse flow of water from a contaminated source back into the clean water supply. It is typically installed at key points in the plumbing system where there is a risk of cross-contamination. Backflow can occur when there is a sudden drop in water pressure, causing water to flow in the opposite direction. This reversal of flow can happen due to various reasons, such as a burst pipe, a water main break, or even a nearby fire hydrant being used. Without a backflow preventer, this contaminated water could re-enter the main water supply and pose a serious health risk.
Backflow preventers work by utilizing a combination of valves and check mechanisms to ensure that water flows in only one direction. The most common type of backflow preventer is the reduced pressure zone (RPZ) device. This device consists of two independently operating check valves and a relief valve. When water flows in the correct direction, the check valves remain open, allowing water to pass through. However, if there is a reversal in water flow, the check valves close, blocking any contaminated water from entering the clean water supply. The relief valve, on the other hand, is designed to release excess pressure and ensure the proper functioning of the backflow preventer.
The importance of water quality
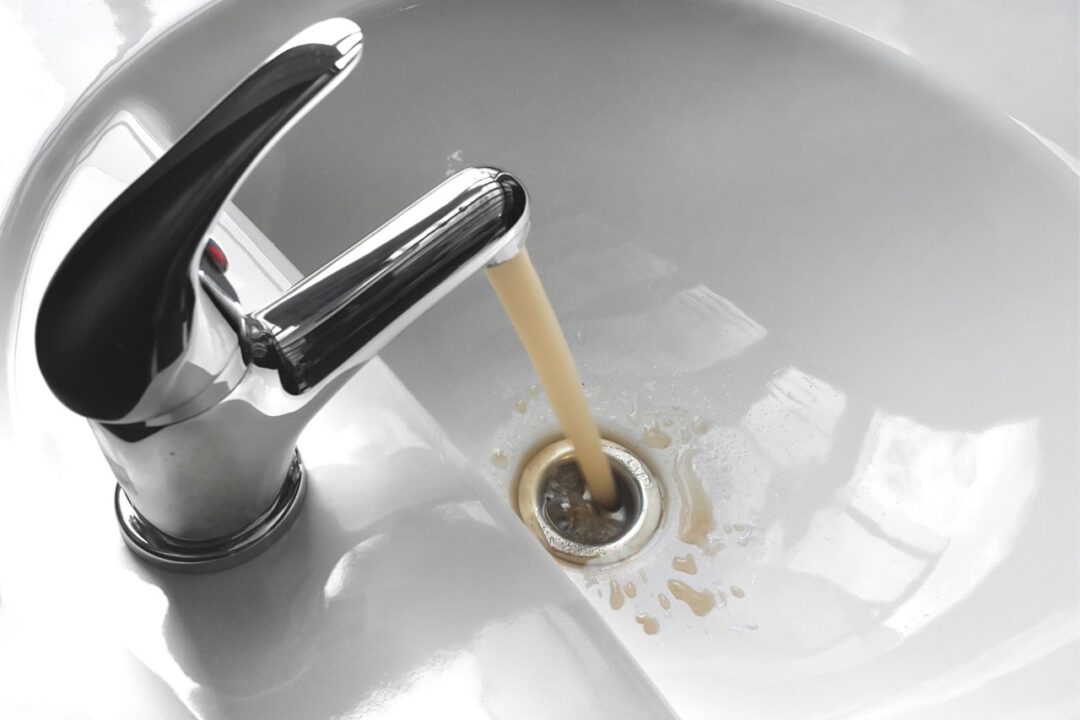

Ensuring the quality of our water is of utmost importance for our health and well-being. Contaminated water can harbor harmful bacteria, chemicals, and other pollutants that can cause a wide range of health issues. Backflow preventers play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the water supply by preventing the contamination of clean water sources.
In addition to protecting our health, maintaining water quality is also vital for the proper functioning of various industries and businesses. For example, in the food and beverage industry, contaminated water can lead to product spoilage and pose a risk to consumer safety. In hospitals and healthcare facilities, clean water is essential for patient care and infection control. Even in our homes, having access to clean water is essential for our daily activities.
By installing backflow preventers, we can ensure that the water flowing into our homes, businesses, and public facilities remains clean and safe for use. These devices act as a reliable barrier, preventing the backflow of contaminated water and safeguarding our health and the integrity of our water supply.
How backflow preventers work
Backflow preventers rely on a combination of mechanical components to ensure that water flows in one direction only. The specific mechanism may vary depending on the type of backflow preventer, but the principle remains the same – to prevent the reverse flow of water.
Reduced pressure zone (RPZ) backflow preventers, as mentioned earlier, are one of the most common types used in plumbing systems. These devices employ two check valves and a relief valve to prevent backflow. When water is flowing in the correct direction, both check valves remain open, allowing water to pass through. However, if there is a drop in pressure or a reversal in water flow, the check valves close, creating a barrier that prevents contaminated water from entering the clean water supply. The relief valve is responsible for releasing excess pressure and ensuring the proper functioning of the backflow preventer.
Another type of backflow preventer is the double check valve assembly (DCVA). This device consists of two check valves that operate independently. Similar to RPZ backflow preventers, the check valves in DCVAs close when there is a reversal in water flow, effectively blocking any contaminated water from entering the clean water supply.
Both RPZ backflow preventers and DCVAs are designed to provide reliable protection against backflow, but their suitability depends on the specific application and local regulations. It is essential to consult with a qualified professional to determine the most appropriate type of backflow preventer for your needs.
Types of backflow preventers

Backflow preventers come in various types, each designed to address specific needs and requirements. The choice of backflow preventer depends on factors such as the level of protection required, the type of application, and local regulations. Some common types of backflow preventers include:
- Reduced pressure zone (RPZ) backflow preventers: These are the most commonly used backflow preventers in residential, commercial, and industrial applications. They provide a high level of protection by utilizing two check valves and a relief valve.
- Double check valve assembly (DCVA): DCVAs are typically used in low-risk applications where a moderate level of protection is required. They consist of two check valves that operate independently.
- Pressure vacuum breaker (PVB): PVB backflow preventers are commonly used in outdoor irrigation systems. They rely on a spring-loaded check valve and an air inlet valve to prevent backflow.
- Atmospheric vacuum breaker (AVB): AVBs are frequently used in sprinkler systems and other low-risk applications. They rely on a poppet-style check valve and an air inlet valve to prevent backflow.
- Spill-resistant vacuum breaker (SVB): SVBs are primarily used in portable water containers, such as hoses and outdoor faucets. They are designed to prevent backflow during the filling process.
The choice of backflow preventer depends on the specific requirements of your plumbing system and the level of protection needed. It is essential to consult with a qualified professional to ensure that the backflow preventer you choose meets the necessary regulatory standards and provides adequate protection for your water supply.
Common causes of backflow
Backflow can occur due to various reasons, and understanding these causes is crucial in preventing contamination of the water supply. Some common causes of backflow include:
- Backsiphonage: Backsiphonage occurs when there is a sudden drop in water pressure, causing water to flow in the opposite direction. This can happen if a nearby fire hydrant is being used or if there is a break in the water main. Backsiphonage can also occur if there is a significant demand for water in the system, such as during firefighting or water main repairs.
- Backpressure: Backpressure occurs when the pressure in the plumbing system exceeds the pressure in the main water supply. This can happen if a pump or other pressurized equipment is connected to the plumbing system. Backpressure can force contaminated water, chemicals, or other pollutants to flow back into the clean water supply.
- Cross-connection: A cross-connection is a physical connection between the clean water supply and a potential source of contamination, such as a chemical tank or irrigation system. If a cross-connection exists and there is a drop in water pressure, contaminated water can flow back into the clean water supply, posing a health risk.
By understanding the common causes of backflow, we can take proactive measures to prevent contamination of the water supply. Installing backflow preventers at key points in the plumbing system and regularly maintaining them can help mitigate the risk of backflow and ensure the continued delivery of clean and safe water.
Backflow preventer installation and maintenance
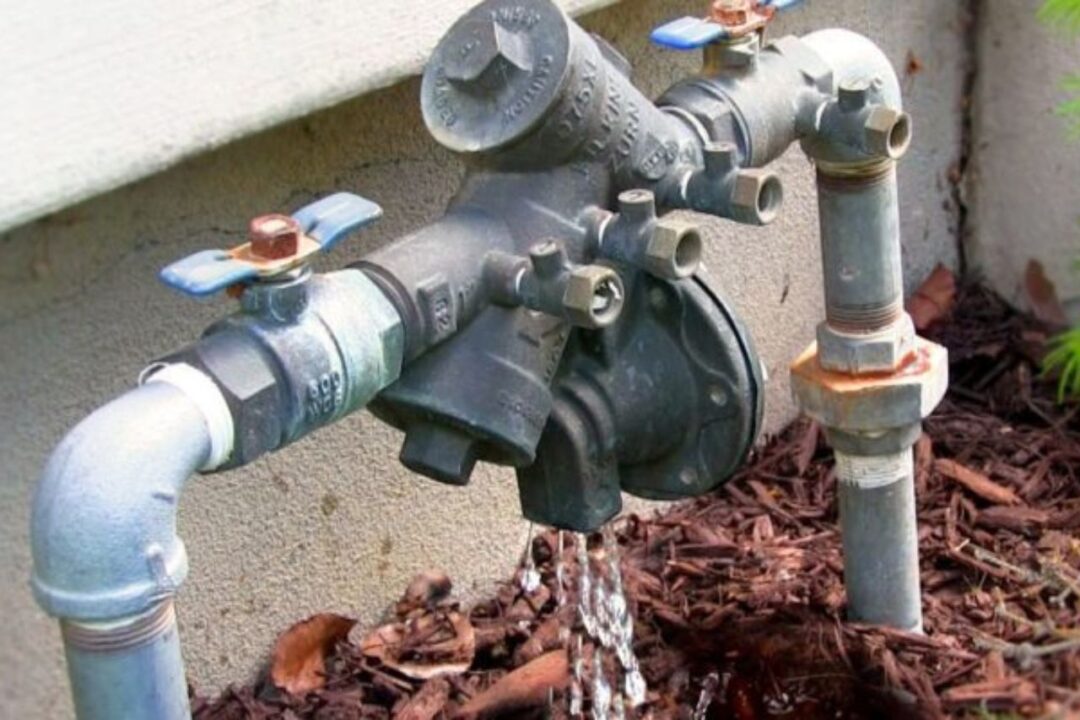

Proper installation and regular maintenance of backflow preventers are essential to ensure their effectiveness and longevity. It is crucial to hire a qualified professional to install the backflow preventer, as improper installation can compromise its functionality and put the water supply at risk.
During installation, the backflow preventer should be placed at the appropriate location in the plumbing system, following the manufacturer’s guidelines and local regulations. The device should be properly sized to handle the expected flow rate and pressure conditions. Additionally, all connections and fittings should be secure and leak-free to prevent any potential points of backflow.
Once installed, backflow preventers should be regularly inspected and tested to ensure their proper functioning. Most jurisdictions require annual testing of backflow preventers by a certified professional. During the testing process, the professional will check for any signs of wear or damage, test the operation of the check valves and relief valve, and verify that the backflow preventer meets the necessary regulatory standards. Any necessary repairs or replacements should be promptly addressed to maintain the integrity of the water supply.
In addition to regular testing, it is important to keep the backflow preventer and its surrounding area clean and free from debris. Regularly inspect the device for any signs of leaks, corrosion, or damage. If any issues are detected, they should be addressed immediately to prevent the risk of backflow.
Signs of a faulty backflow preventer
A faulty backflow preventer can compromise the safety and quality of the water supply. It is important to be aware of the signs that may indicate a problem with the backflow preventer. Some common signs of a faulty backflow preventer include:
- Decreased water pressure: A sudden decrease in water pressure can indicate a problem with the backflow preventer. This could be a sign that the check valves are not closing properly, allowing water to flow in the wrong direction.
- Contaminated water: If you notice a change in the color, taste, or odor of your water, it could be a sign of backflow. Contaminated water can indicate that the backflow preventer is not effectively blocking the reverse flow of water.
- Leaks or dripping: Any signs of leaks or dripping around the backflow preventer should be taken seriously. Leaks can indicate a problem with the valves or fittings, compromising the effectiveness of the device.
- Excessive pressure: If you notice unusually high water pressure in your plumbing system, it could be a sign of backflow. Excessive pressure can put stress on the backflow preventer, affecting its ability to function properly.
If you observe any of these signs, it is important to contact a qualified professional to inspect and repair the backflow preventer. Prompt action can help prevent further damage and ensure the continued protection of your water supply.
The role of backflow preventers in protecting public health
Backflow preventers play a vital role in protecting public health by preventing the contamination of the water supply. By stopping the reverse flow of water, these devices act as a barrier, keeping pollutants, chemicals, and other harmful substances from seeping back into the clean water supply.
In addition to protecting public health, backflow preventers also have economic benefits. Contaminated water can lead to costly damages, such as product spoilage, equipment damage, and increased healthcare costs. By investing in backflow preventers, we can minimize the risk of contamination and avoid the financial burdens associated with waterborne illnesses and damages.
To ensure the effectiveness of backflow preventers in protecting public health, it is essential to have proper regulations and certifications in place. Local jurisdictions often have specific requirements for the installation, testing, and maintenance of backflow preventers. Compliance with these regulations helps ensure that backflow preventers are installed correctly, regularly inspected, and maintained to the highest standards.
Backflow preventer regulations and certifications

Backflow preventers are subject to various regulations and certifications to ensure their proper functioning and effectiveness. These regulations vary by jurisdiction and may include requirements for the installation, testing, and maintenance of backflow preventers.
In the United States, the American Society of Sanitary Engineering (ASSE) and the International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials (IAPMO) are two prominent organizations that establish standards for backflow preventers. These organizations provide certifications for professionals who install, test, and maintain backflow preventers, ensuring that they have the necessary knowledge and expertise to perform these tasks effectively.
It is important to work with a certified professional when installing, testing, or maintaining a backflow preventer. These professionals have undergone the necessary training and have the expertise to ensure that the backflow preventer meets the required standards and provides adequate protection for the water supply.
Conclusion
Water is a precious resource that we rely on for our daily needs. Ensuring the quality and safety of our water supply is crucial for our health, well-being, and the proper functioning of various industries. Backflow preventers play a critical role in protecting our water quality by preventing the contamination of the water supply.
By understanding how backflow preventers work, the types available, and the common causes of backflow, we can take proactive measures to safeguard our water supply. Proper installation, regular maintenance, and compliance with regulations and certifications are essential in ensuring the effectiveness of backflow preventers.
Whether in our homes, businesses, or public facilities, backflow preventers are unsung heroes that work silently in the background, protecting our water quality and ensuring a healthy and safe environment for all. Let’s appreciate these ingenious devices and make informed decisions to maintain clean and healthy water for ourselves and future generations.







