Troubleshoot Bad Anode Rod Symptoms
Are you experiencing strange odors or discoloration in your water? It could be a sign of a larger issue with your water heater.
A crucial component of your water heater is the anode rod, which protects the tank from corrosion. When it becomes faulty, it can lead to various problems, including smelly water, rusty water, and reduced efficiency.
Understanding the role of the anode rod and recognizing the signs of its failure can help you troubleshoot issues with your water heater and take corrective action.
Key Takeaways
- Identify common issues caused by a faulty anode rod.
- Understand the importance of the anode rod in water heaters.
- Recognize the signs of anode rod failure.
- Learn how to troubleshoot water heater issues.
- Discover the benefits of maintaining a healthy anode rod.
Understanding the Purpose of Anode Rods in Water Heaters
Anode rods are sacrificial rods that attract corrosive elements in the water, thereby protecting the water heater tank. This crucial component is designed to extend the lifespan of your water heater by taking the brunt of corrosive damage. Understanding how anode rods work and the different types available is essential for maintaining your water heater’s efficiency and longevity.
What Is an Anode Rod and How Does It Work?
An anode rod is typically made of a more corrosive material than the water heater tank itself, such as magnesium, aluminum, or a zinc-aluminum alloy. By attracting corrosive elements, the anode rod protects the tank from rust and damage, ensuring that your water heater continues to function properly. Regular inspection of the anode rod is crucial to determine if it needs replacement.
Types of Anode Rods and Their Differences
There are several types of anode rods available, each with its unique characteristics and benefits.
Magnesium Anode Rods
Magnesium anode rods are the most common type and are known for their high level of corrosion protection. They are particularly effective in soft water conditions.
Aluminum Anode Rods
Aluminum anode rods are a good option for areas with hard water, as they are less prone to rapid corrosion compared to magnesium rods in such conditions.
Zinc Aluminum Alloy Anode Rods
Zinc aluminum alloy anode rods offer a balanced performance, providing good corrosion protection while being less expensive than some other materials. They are suitable for a wide range of water conditions.
The Importance of a Functioning Anode Rod
The anode rod plays a vital role in protecting your water heater from corrosion. It is a sacrificial component designed to attract corrosive elements in the water, thereby safeguarding the tank.
How Anode Rods Protect Your Water Heater
Anode rods work by corroding in place of the water heater tank. This sacrificial action helps extend the lifespan of the water heater. Magnesium, aluminum, and zinc are common materials used for anode rods, each with its own benefits and drawbacks.
- Magnesium anode rods are highly effective in soft water conditions.
- Aluminum anode rods offer a good balance between protection and cost.
- Zinc anode rods are often used in areas with high sulfate levels in the water.
Typical Lifespan of Anode Rods
The lifespan of an anode rod can vary significantly based on several factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for maintaining your water heater’s health.
Factors Affecting Anode Rod Longevity
Key factors include water hardness, temperature settings, and the presence of corrosive elements in the water. Hard water, for instance, can significantly reduce the lifespan of an anode rod.
Average Replacement Timeframes
Typically, anode rods need to be inspected every 3 to 5 years. Replacement is usually necessary when the rod is significantly corroded or depleted. Regular checks can help identify warning signals of faulty anode rod early on.
By understanding the importance of a functioning anode rod and recognizing the signs that indicate its failure, you can take proactive steps to maintain your water heater’s efficiency and extend its lifespan.
Bad Anode Rod Symptoms: Primary Warning Signs
When your anode rod begins to deteriorate, it can cause a range of problems that are easily detectable. Being aware of these signs can help you address the issue before it leads to more significant damage to your water heater.
Rusty or Discolored Water
One of the most common indicators of a failing anode rod is the presence of rusty or discolored water coming from your faucets. This discoloration is often a result of the anode rod corroding and releasing particles into the water supply. If you notice that your water has become consistently rusty or has an unusual color, it’s a good idea to inspect your anode rod.
Sulfur Smell or Rotten Egg Odor
A sulfur smell or “rotten egg” odor from your hot water is another sign that your anode rod may be deteriorating. This smell is typically caused by bacteria that thrive in the warm, nutrient-rich environment provided by a corroding anode rod. If you notice this odor, it’s essential to check your anode rod’s condition.
Unusual Noises from Your Water Heater
Unusual noises coming from your water heater, such as banging, clanking, or rumbling sounds, can also indicate anode rod failure. These noises are often due to sediment buildup or the effects of corrosion on the water heater’s components. Inspecting your anode rod can help determine if it’s the source of these noises.
By being aware of these primary warning signs, you can take proactive steps to maintain your water heater and potentially extend its lifespan. Regularly checking your anode rod and addressing any issues promptly is key to avoiding more costly repairs down the line.
Secondary Signs of Anode Rod Deterioration
As the anode rod in your water heater continues to deteriorate, several secondary signs may indicate its failing condition. These signs are crucial for early detection and prevention of further damage to your water heater.
Reduced Hot Water Efficiency
A deteriorating anode rod can lead to reduced hot water efficiency. When the anode rod is in poor condition, the water heater has to work harder to heat water, resulting in increased energy bills and longer wait times for hot water.
Metallic Taste in Water
Another secondary sign is a metallic taste in the water. As the anode rod corrodes, it can contaminate the water with metallic ions, affecting its taste and quality. This is not only unpleasant but can also be a health concern.
Visible Corrosion on Water Heater Components
Visible corrosion on the water heater’s components is a clear indicator of anode rod deterioration. When the anode rod fails, the water heater’s tank and other parts become susceptible to corrosion, which can lead to leaks and other serious issues.
Recognizing these secondary signs of anode rod deterioration can help you take timely action to replace the anode rod and maintain your water heater’s efficiency and longevity.
How to Inspect Your Water Heater’s Anode Rod
Inspecting your water heater’s anode rod is a crucial maintenance task that can extend the lifespan of your water heater. Regular inspections can help identify potential issues before they become major problems.
Tools Needed for Inspection
To inspect your anode rod, you’ll need a few basic tools. These include a socket wrench or breaker bar, a new hex head or socket that fits your anode rod, and some Teflon tape for reinstallation. Having these tools on hand will make the inspection process smoother.
Step-by-Step Inspection Process
The inspection process involves several key steps:
Shutting Off Power and WaterEnsure the power to your water heater is turned off at the circuit breaker or fuse box. Also, shut off the water supply to prevent any leaks or flooding.
Accessing and Removing the Anode RodLocate the anode rod on top of your water heater. Use your socket wrench or breaker bar to remove it. Be prepared for some resistance.
Visual Examination TechniquesOnce removed, inspect the anode rod visually. Look for signs of wear, corrosion, or depletion. A rod that is heavily corroded or significantly depleted needs to be replaced.
What to Look for During Inspection
During the inspection, pay attention to the anode rod’s condition. Check if it’s heavily corroded or worn down. If more than half of the rod is gone, it’s time for a replacement.
Regular inspections can help you catch issues early, potentially saving you from more costly repairs. By following these steps, you can ensure your water heater remains in good condition.
Interpreting What You Find: Anode Rod Condition Assessment
After inspecting your water heater’s anode rod, it’s crucial to understand what you’re looking at to determine its condition. The anode rod’s state can give you valuable insights into your water heater’s health and help you decide if a replacement is necessary.
Signs of Normal Wear vs. Problematic Deterioration
A certain level of wear on the anode rod is normal, but significant deterioration can be a sign of a problem. Normal wear might include a reduction in the rod’s diameter or some surface corrosion. However, if the rod is heavily corroded, fragmented, or significantly depleted, it indicates problematic deterioration.
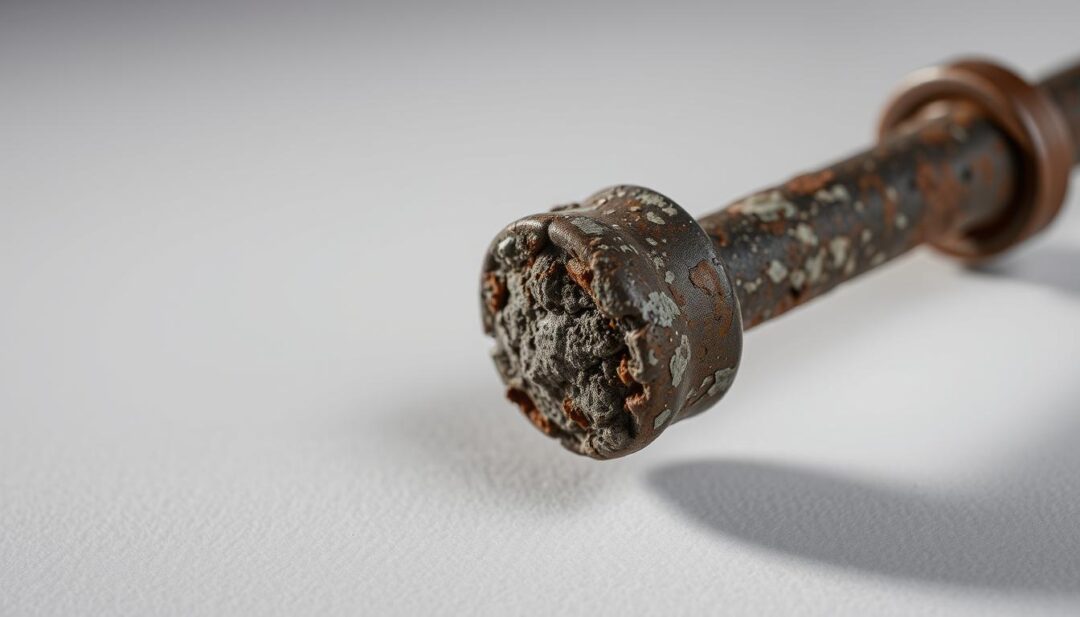

When Replacement Is Necessary
If your inspection reveals significant corrosion or depletion of the anode rod, replacement is likely necessary. Additionally, if you notice any signs of rust or corrosion on other parts of your water heater, it may be a sign that the anode rod is no longer functioning correctly, and replacement should be considered to prevent further damage.
The Process of Replacing an Anode Rod
Understanding how to replace an anode rod is vital for maintaining your water heater’s efficiency and prolonging its lifespan. Replacing a corroded anode rod is a relatively straightforward process that requires some basic tools and precautions.
Tools and Materials Required
Before starting the replacement process, gather the necessary tools and materials. You’ll need a socket wrench or breaker bar, a suitable socket to fit the anode rod, Teflon tape, and a new anode rod compatible with your water heater model.
- Socket wrench or breaker bar
- Appropriate socket
- Teflon tape
- New anode rod
Step-by-Step Replacement Guide
Preparation Steps
First, turn off the power supply to your water heater. For electric heaters, switch off the breaker or remove the fuse. For gas heaters, set the thermostat to “pilot.” Allow the water to cool down before proceeding.
Removal of Old Anode Rod
Use a socket wrench or breaker bar to loosen and remove the old anode rod. Be prepared for some water spillage when the rod is removed.
Installation of New Anode Rod
Wrap Teflon tape around the threads of the new anode rod to prevent leaks. Insert the new rod and tighten it securely using your socket wrench.
Safety Precautions During Replacement
Always wear protective gloves and eyewear when working with tools and potentially hazardous materials. Ensure the area is well-ventilated, and consider having a fire extinguisher nearby.
By following these steps, you can successfully replace your water heater’s anode rod, helping to prevent corrosion and extend the unit’s lifespan. Regularly checking and maintaining your anode rod is a simple yet effective way to ensure your water heater operates efficiently and safely.
Choosing the Right Replacement Anode Rod
The key to prolonging your water heater’s lifespan lies in choosing the appropriate anode rod replacement. This decision significantly impacts the longevity and efficiency of your water heater.
Material Options: Magnesium, Aluminum, and Zinc
Anode rods are made from various materials, each with its benefits. Magnesium anode rods are highly effective in protecting water heaters but may react with certain water chemistries. Aluminum rods are a good alternative, offering a balance between protection and cost. Zinc anodes are less common but are used in specific applications, particularly where water is softer.
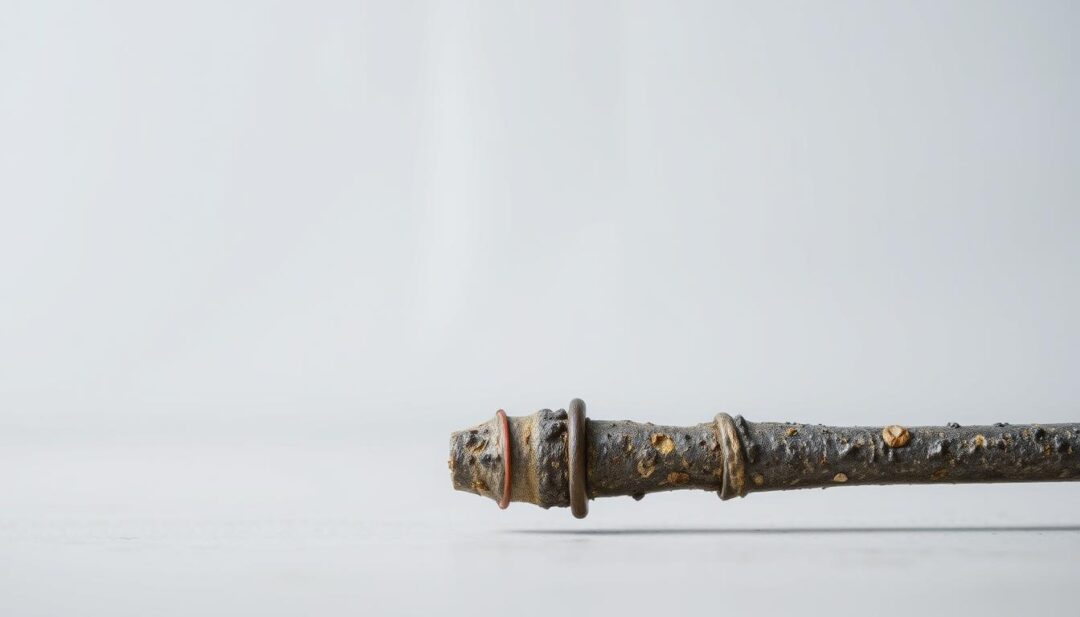

Size and Compatibility Considerations
Ensuring the replacement anode rod is the correct size and compatible with your water heater is crucial. Factors to consider include the rod’s length, diameter, and thread type.
Standard vs. Flexible Anode Rods
Standard anode rods are rigid and straightforward to install, while flexible anode rods can be bent to fit into tight spaces, making them ideal for water heaters with complex configurations.
Length and Diameter Guidelines
| Water Heater Size | Recommended Anode Rod Diameter | Recommended Anode Rod Length |
|---|---|---|
| 30-40 gallons | 3/4 inch | 40-50 inches |
| 50-80 gallons | 1 inch | 50-60 inches |
By considering these factors and choosing the right material and size, you can effectively protect your water heater from corrosion and prolong its lifespan, addressing signs of deteriorating anode rod functionality.
DIY vs. Professional Anode Rod Replacement
The decision to replace an anode rod yourself or hire a professional plumber depends on several key factors, including your comfort level with DIY projects, the complexity of the installation, and your budget.
When You Can Handle It Yourself
If you’re comfortable with basic plumbing tasks and have experience with DIY projects, replacing an anode rod can be a manageable task. To do it successfully, you’ll need to ensure you have the correct replacement rod and follow the manufacturer’s instructions. Proper inspection and preparation are crucial to avoid any complications during the replacement process.
When to Call a Professional Plumber
There are situations where hiring a professional plumber is the best course of action. If you’re unsure about the type of anode rod your water heater requires or if you encounter any difficulties during the inspection, it’s wise to seek professional help.
Complex Installation Scenarios
In cases where the anode rod is particularly difficult to access or if your water heater has a complex configuration, a professional plumber’s expertise can be invaluable. They have the necessary tools and experience to handle such scenarios efficiently.
Cost Comparison: DIY vs. Professional Service
While DIY replacement can save you money on labor costs, it’s essential to consider the potential risks and additional costs associated with improper installation. Hiring a professional plumber may seem more expensive upfront, but it ensures the job is done correctly, potentially saving you from future complications and expenses.
Consequences of Ignoring Bad Anode Rod Symptoms
Ignoring the warning signals of a faulty anode rod can lead to severe consequences for your water heater. The anode rod plays a crucial role in protecting your water heater from corrosion, and when it fails, the repercussions can be significant.
When the anode rod deteriorates, it can no longer effectively safeguard the water heater tank. This can lead to a range of issues, including a reduced water heater lifespan and increased risk of costly repairs.
Impact on Water Heater Lifespan
A corroded water heater anode rod can significantly shorten the lifespan of your water heater. When the anode rod is no longer functioning correctly, the tank begins to corrode, leading to premature failure. Replacing a water heater can be a costly and inconvenient process, making it essential to address anode rod issues promptly.
Potential Repair Costs and Complications
The consequences of ignoring a bad anode rod can also include potential repair costs and complications. As the anode rod deteriorates, it can cause damage to other components of the water heater, leading to costly repairs. In some cases, the damage can be so severe that it may be more cost-effective to replace the water heater entirely.
| Consequence | Description | Potential Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced Water Heater Lifespan | Premature failure due to corrosion | $800 – $1,200 |
| Costly Repairs | Damage to other water heater components | $200 – $500 |
| Water Heater Replacement | Complete replacement of the water heater | $800 – $1,500 |
By understanding the consequences of ignoring bad anode rod symptoms, homeowners can take proactive steps to maintain their water heaters and avoid costly repairs. Regular inspection and replacement of the anode rod can help extend the lifespan of the water heater and prevent potential complications.
Conclusion
Recognizing bad anode rod symptoms is crucial for extending the lifespan of your water heater. By understanding the signs of anode rod deterioration, such as rusty water, unusual noises, or a metallic taste, you can take proactive steps to replace it when necessary.
Regular inspection and timely anode rod replacement signs can prevent costly repairs and ensure your water heater operates efficiently. Whether you choose to replace the anode rod yourself or hire a professional, addressing the issue promptly is key to maintaining your water heater’s overall health.
By staying vigilant and addressing anode rod issues early, you can enjoy a reliable supply of hot water while minimizing the risk of complications. This proactive approach will help you get the most out of your water heater.