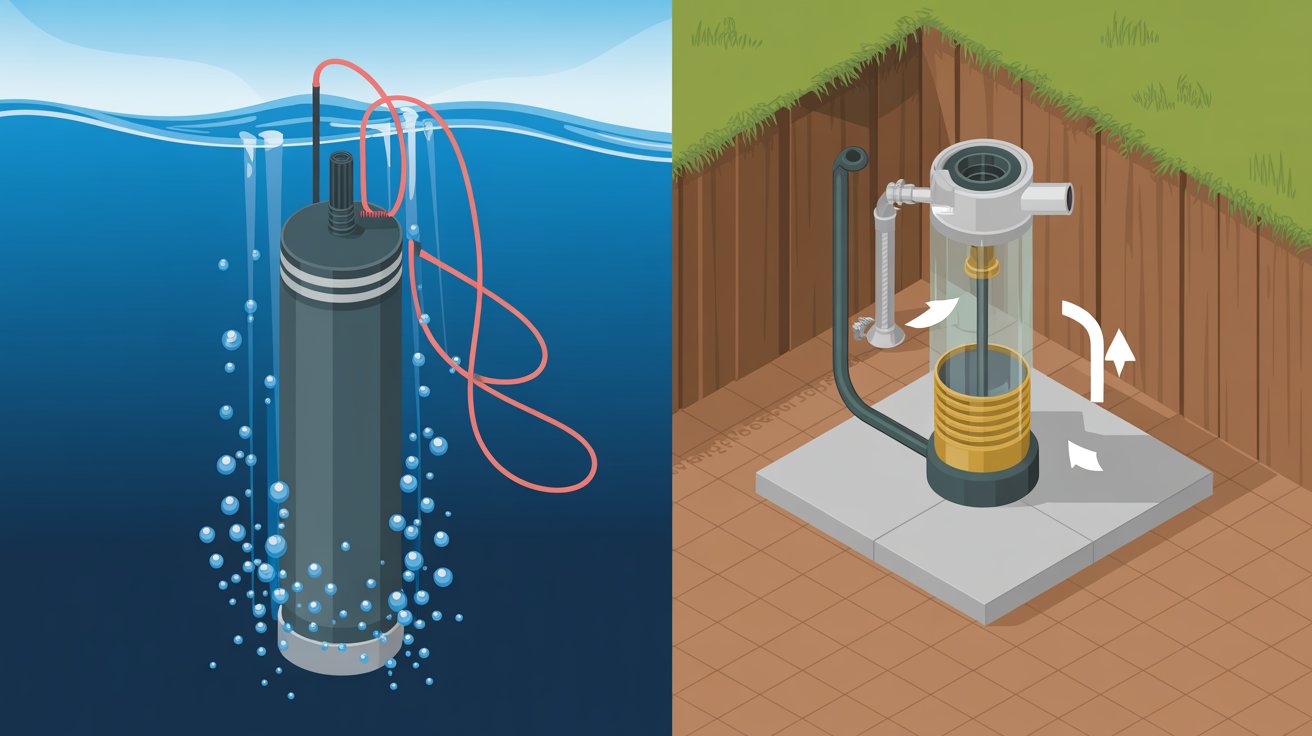
Submersible Water Pump vs Jet Pump: The Pros and Cons
Are you torn between choosing a submersible or jet pump for your home? Many homeowners scratch their heads when looking at their water pumping system and wonder if there’s a better option.
Selecting the right pump is crucial for efficient water supply and minimizing energy costs. In this article, we’ll compare the pros and cons of submersible pumps and jet pumps, helping you make an informed decision for your home’s needs.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the differences between submersible and jet pumps.
- Evaluating the pros and cons of each pump type.
- Factors to consider when choosing the right pump for your home.
- Energy efficiency and cost implications of each pump.
- Maintenance requirements for submersible and jet pumps.
Understanding Water Pumps for Home Use
Water pumps play a vital role in supplying water to homes, especially those relying on wells or boreholes. The decision between jet pumps and submersible pumps is critical for ensuring a reliable and efficient water supply.
The Role of Water Pumps in Residential Water Systems
Water pumps are essential in residential water systems as they are responsible for drawing water from the source and distributing it throughout the home. A reliable water pump ensures a consistent water supply, which is crucial for daily household needs. The type of pump used can significantly affect the system’s overall efficiency and performance.
“A good pump is the heart of any water system,” as it directly impacts the water pressure and flow rate. Homeowners must consider their specific needs, including the depth of their well and the household’s water demand.
Key Factors in Pump Selection for Homeowners
When selecting a water pump, homeowners should consider several key factors, including the well depth, water demand, and power supply. The depth of the well is particularly important, as it determines whether a jet pump or a submersible pump is more suitable. Additionally, the household’s water demand, including the number of occupants and water-using appliances, should be assessed to ensure the chosen pump can meet these needs.
- Well depth and water level
- Household water demand
- Power supply and energy efficiency
By carefully evaluating these factors, homeowners can make an informed decision when choosing between a jet pump and a submersible pump, ensuring their residential water system operates efficiently and effectively.
What Is a Submersible Water Pump?
Submersible pumps are designed to be submerged in water, offering a reliable solution for extracting water from wells and other sources. These pumps are typically long and narrow, allowing them to fit inside well casings as small as 5 or 6 inches in diameter.
Design and Operating Principles
The design of a submersible water pump is centered around its ability to operate underwater. Sealed motors and hermetically sealed electrical connections prevent water ingress, ensuring safe and efficient operation. The pump’s motor is connected to a pump end that is designed to push water upwards, creating pressure to supply water to the surface.
Efficient operation is achieved through the use of multiple stages of impellers and diffusers, which increase the pressure of the water being pumped. This design allows submersible pumps to lift water from considerable depths.
Types of Submersible Pumps
Submersible pumps are categorized based on their application and the depth at which they operate.
Deep Well Submersible Pumps
These pumps are designed for deep well applications, capable of lifting water from depths of over 200 feet. Their long, narrow design fits into smaller diameter wells.
Shallow Well Submersible Pumps
Used for shallower wells, these pumps are suitable for water tables that are closer to the surface. They are often more compact and can be used in a variety of residential water supply systems.
Common Applications for Submersible Pumps
Submersible pumps are versatile and are used in various applications, including:
- Residential water supply systems
- Irrigation systems
- Industrial water supply
- Drinking water wells
A comparison of submersible pump applications can be seen in the table below:
| Application | Typical Depth | Pump Type |
|---|---|---|
| Residential Water Supply | 0-200 feet | Shallow or Deep Well |
| Irrigation | 50-500 feet | Deep Well |
What Is a Jet Pump?
In the realm of water pumping, jet pumps stand out for their ability to efficiently draw water from wells and other sources. A jet pump operates by using a combination of suction and pressure to lift water from its source to the surface, making it a versatile solution for various water supply needs.
Design and Operating Principles
Jet pumps are similar to other types of pumps in that they have a motor that spins one or more pump impellers to cause water to flow under pressure. The unique aspect of a jet pump lies in its use of a jet assembly, which includes a nozzle and a venturi, to create the suction needed to draw water from the well. This design allows jet pumps to be effective for both shallow and deep well applications.
The operating principle of a jet pump involves creating a pressure differential that facilitates the flow of water. As the impeller spins, it creates a region of low pressure near the jet assembly, drawing water into the pump. The water is then pressurized and discharged through the outlet, providing a steady supply of water.
Single-Stage vs. Convertible Jet Pumps
Jet pumps are available in different configurations, including single-stage and convertible models. Single-stage jet pumps are designed for shallow well applications and are typically less expensive. They are suitable for wells with a depth of up to 25 feet.
Convertible jet pumps, on the other hand, offer more flexibility as they can be adjusted for use in either shallow or deep wells. This makes them a more versatile option for homeowners who may need to adapt their pumping solution to different well depths.
Shallow Well Jet Pumps
Shallow well jet pumps are designed for wells with a depth of up to 25 feet. They are typically single-stage pumps and are less expensive than their convertible counterparts.
Deep Well Jet Pumps
Deep well jet pumps, often convertible models, are used for wells deeper than 25 feet. They require more power to operate and are capable of handling greater depths.
Common Applications for Jet Pumps
Jet pumps are commonly used in residential and commercial settings for water supply. They are particularly suitable for shallow wells and are known for their ease of installation and maintenance.
The versatility of jet pumps makes them a popular choice for various applications, including irrigation, livestock watering, and domestic water supply.
Submersible Water Pump vs Jet Pump: Direct Comparison
Both submersible and jet pumps have their pros and cons, which become apparent when comparing their performance and efficiency. This section will delve into the key differences between these two types of pumps, helping you make an informed decision for your water pumping needs.
Performance and Pumping Capacity
When it comes to performance, submersible water pumps generally outperform jet pumps, especially in deep well applications. Submersible pumps can push water to the surface from greater depths without a significant drop in pressure. In contrast, jet pumps may struggle with deeper wells due to their reliance on suction lift.
Submersible pumps are designed to operate underwater, which allows them to push water to the surface more efficiently. Jet pumps, on the other hand, are typically installed above ground and use a combination of suction and pressure to move water.
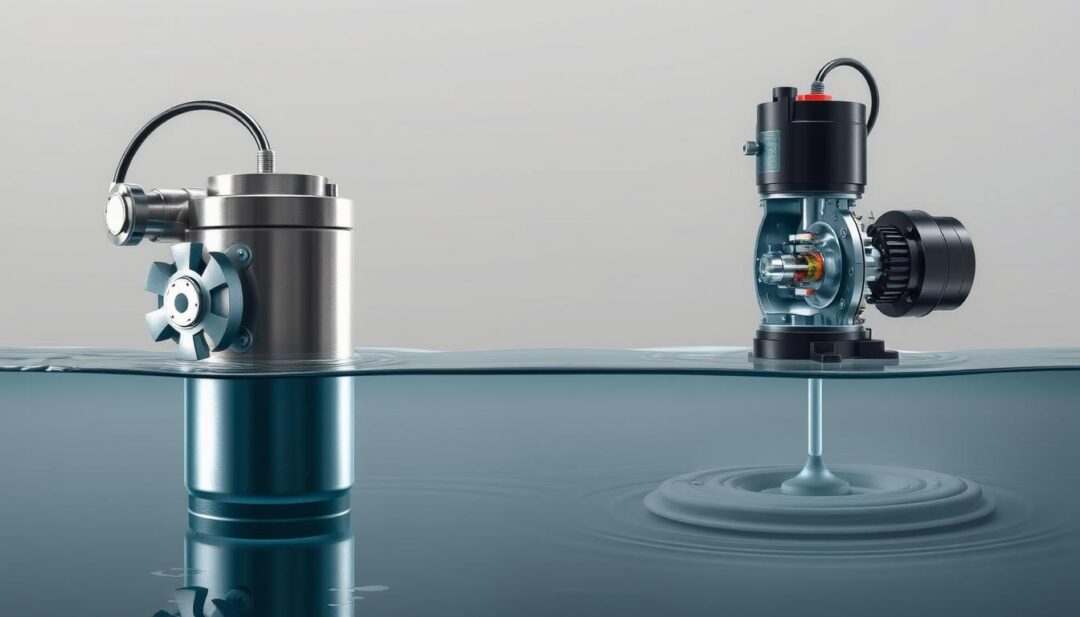

Energy Efficiency and Power Consumption
Submersible pumps are known for their energy efficiency, particularly in deep well applications. They directly push water to the surface, reducing the energy required to overcome the weight of the water column. Jet pumps, while effective for shallower wells, may consume more energy due to the inefficiencies in their suction-based operation.
Data supports that submersible well pumps win the efficiency contest every single time, making them a cost-effective choice in the long run.
Noise Levels and Operation
One of the significant advantages of submersible pumps is their quiet operation. Being submerged underwater, they produce less noise compared to jet pumps, which can be quite loud due to their above-ground installation and mechanical operation.
Durability and Lifespan
Submersible pumps tend to have a longer lifespan compared to jet pumps, mainly because they are protected from environmental factors like temperature fluctuations and are less prone to cavitation. Their robust design and operation underwater contribute to their durability.
In contrast, jet pumps are more exposed and can be affected by various environmental conditions, potentially reducing their lifespan.
Pros and Cons of Submersible Pumps
The decision to install a submersible pump depends on understanding its benefits and drawbacks. Submersible pumps are widely used for their efficiency and reliability in pumping water from deep wells and other applications.
Advantages of Submersible Pumps
Submersible pumps offer several key advantages that make them a preferred choice for many users.
Higher Efficiency and Less Prone to Cavitation
Submersible pumps are more efficient than jet pumps and less prone to cavitation, which can damage the pump over time. This efficiency is due to their design, which pushes water up from the well rather than pulling it, reducing the risk of cavitation.
No Priming Required and Quieter Operation
These pumps do not require priming, as they are submerged in water and can start pumping immediately. Additionally, they operate more quietly than jet pumps since the noise is dampened by the surrounding water and earth.
Less Affected by Flooding and Weather
Being submerged, submersible pumps are less affected by surface weather conditions and flooding, making them a reliable choice for areas prone to such conditions.
Disadvantages of Submersible Pumps
Despite their advantages, submersible pumps also have some drawbacks that need to be considered.
Higher Initial Cost and Installation Complexity
The initial cost of a submersible pump can be higher than that of a jet pump, and the installation process is often more complex, requiring specialized knowledge and equipment.
More Difficult Access for Repairs
Since submersible pumps are located underwater, accessing them for repairs can be challenging and costly, potentially leading to longer downtime.
Potential for Overheating
If not properly maintained or if operated under certain conditions, submersible pumps can be prone to overheating, which can reduce their lifespan.
Pros and Cons of Jet Pumps
When considering a pump for your home, understanding the pros and cons of jet pumps is essential. Jet pumps are a viable option for many residential water systems, offering a balance of performance and cost. However, like any technology, they have their advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of Jet Pumps
Jet pumps have several benefits that make them an attractive choice for homeowners. These advantages include lower initial costs, easier maintenance, and versatility in different well depths.
Lower Initial Cost and Easier Installation
One of the significant advantages of jet pumps is their lower initial cost compared to submersible pumps. Additionally, jet pumps are typically easier to install since they are located above ground, making the installation process more straightforward.
Easier Access for Maintenance
Jet pumps are generally easier to maintain because they are not submerged in water. This accessibility reduces the complexity and cost of maintenance tasks.
Versatility for Different Well Depths
Jet pumps can be used in various well depths, although their efficiency may vary. They are particularly suitable for shallow wells and can be adapted for deeper wells with the right configuration.
Disadvantages of Jet Pumps
Despite their advantages, jet pumps also have several drawbacks. These include lower efficiency, higher electricity costs, priming requirements, noise issues, and limited depth capability.
Lower Efficiency and Higher Electricity Costs
Jet pumps are generally less efficient than submersible pumps, which can result in higher electricity costs over time. This inefficiency is a crucial factor to consider when evaluating the long-term costs of operating a jet pump.
Priming Requirements and Noise Issues
Jet pumps require priming to operate effectively, which can be inconvenient. Additionally, they can be noisier than submersible pumps, potentially causing disturbance.
Limited Depth Capability
Jet pumps have a limited depth capability compared to submersible pumps. They are most effective in shallow to moderate-depth wells.
| Characteristics | Jet Pumps | Submersible Pumps |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
| Maintenance Access | Easier | More Challenging |
| Depth Capability | Limited | Greater |
Best Applications: When to Choose Each Pump Type
Understanding the best applications for submersible and jet pumps can help homeowners make informed decisions about their water systems. The choice between these two types of pumps largely depends on the specific requirements of the well system, including factors such as well depth, water demand, and environmental conditions.
Ideal Scenarios for Submersible Pumps
Submersible pumps are particularly suited for certain conditions. They are ideal for:
Deep Wells Over 25 Feet
Submersible pumps are more efficient for deep wells because they push water to the surface rather than pulling it, which reduces the risk of cavitation and increases efficiency.
High-Demand Water Systems
For homes or farms with high water demands, submersible pumps can provide a consistent and reliable water supply.
Areas Prone to Flooding
Since submersible pumps are underwater, they are less likely to be damaged by flooding, making them a good choice for areas that experience frequent waterlogging.
Ideal Scenarios for Jet Pumps
Jet pumps, on the other hand, have their own set of ideal applications. They are suitable for:
Shallow Wells Under 25 Feet
Jet pumps are more cost-effective and efficient for shallow wells, where they can effectively pull water to the surface.
Budget-Conscious Installations
For those looking to save on initial costs, jet pumps are generally less expensive to purchase and install.
Areas with Minimal Space Constraints
Jet pumps are installed above ground, making them easier to access and maintain in areas where space is not a concern.
“The right pump can make all the difference in the efficiency and reliability of your water system.” Ultimately, the choice between jet pumps and submersible pumps comes down to the specific needs of your well system. By considering factors such as well depth, water demand, and environmental conditions, homeowners can make an informed decision that meets their needs.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
The installation process and ongoing maintenance requirements are key factors to consider when choosing between submersible and jet pumps. Both types of pumps have unique installation and maintenance needs that can impact their performance and lifespan.
Installing Submersible Pumps
Submersible pumps are installed underwater, typically at the bottom of a well or borehole. This requires careful handling to avoid damage during the lowering process. It’s essential to ensure that the pump is properly sized for the well and that all electrical connections are secure and waterproof.
Key considerations for submersible pump installation include:
- Ensuring the pump is correctly sized for the well diameter and depth
- Using appropriate cable and piping materials
- Securing the pump to prevent movement or sinking
Installing Jet Pumps
Jet pumps, on the other hand, are installed above ground, typically in a pump house or basement. They require a suction pipe to be inserted into the well, and the pump must be primed before operation. The installation process is generally less complex than for submersible pumps, but it still requires careful attention to detail.
Important factors for jet pump installation include:
- Proper priming to avoid airlocks
- Correct sizing of the suction pipe
- Adequate ventilation and protection from the elements
Maintenance Requirements and Troubleshooting
Both submersible and jet pumps require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. While submersible pumps are generally considered maintenance-free, they can be more challenging to service due to their underwater location.
Common Submersible Pump Issues
Common issues with submersible pumps include failure to start, low water pressure, and excessive noise. Troubleshooting often involves checking the power supply, inspecting for blockages, and verifying that the pump is properly seated.
Common Jet Pump Issues
Jet pumps can experience issues such as loss of prime, low pressure, and noisy operation. Troubleshooting typically involves checking for leaks, inspecting the impeller, and ensuring that the suction pipe is not clogged.
Comparative Maintenance Requirements:
| Maintenance Aspect | Submersible Pump | Jet Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Service Accessibility | Difficult due to underwater location | Easier due to above-ground installation |
| Common Issues | Failure to start, low water pressure | Loss of prime, low pressure, noise |
| Troubleshooting | Check power supply, inspect for blockages | Check for leaks, inspect impeller, suction pipe |
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Pump for Your Needs
When deciding between a submersible water pump vs jet pump, it’s essential to consider your specific needs and applications. Submersible well pumps are generally the efficient and simple choice for most well applications, offering a reliable solution for homeowners.
In contrast, centrifugal/jet pumps are ideal for pumping water from a storage tank, making them a great option for certain scenarios. By understanding the pros and cons of each pump type, as well as factors such as well depth, water demand, and energy efficiency, you can make an informed decision when choosing between submersible and jet pumps.
Ultimately, the right pump for you will depend on your unique situation and requirements. By considering these factors and understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each pump type, you can select the best pump to meet your needs and ensure a reliable water supply.